[2017 ~ Now]
Machine/Computer Vision is such an Exciting/ Fast-evolving/ Application-practical field and I am delightful to be a part of it ! As a PhD. student under supervision of Professor Richard P. Wildes York University Toronto Canada, my research focuses on video predictive understanding, which includes interesting tasks as Action/Activity Prediction/Anticiption, Video Prediction, Motion Planning, Vehicle/Pedestrian Trajectory tracking and etc. In a word, I do research on exploring the possible future.
[2015-2017]
Before my Ph.D. journey, I worked with Professor Lin Yang at University of Florida (Go Gator !) as a master research assistant. During my stay, we came out some really cool projects towards biomedical imaging understanding (as listed below).
Recent News
Selected Works
On Diverse Asychronous Activity Anticipation
He Zhao, Richard P. Wildes
European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV2020)
>  | We investigate the joint anticipation of long-term activity labels and their corresponding times with the aim of improving both the naturalness and diversity of predictions. We address these matters using Conditional Adversarial Generative Networks for Discrete Sequences. Central to our approach is a reexamination of the unadvoidable sample quality vs. diversity tradeoff of the recently emerged Gumbel-Softmax relaxation based on discrete data. In particular, we ameliorate this trade-off with a simple but effective sample distance regularizer. Moreover, we provide a unified approach to inference of activity labels and their times so that a single integrated optimization succeeds for both. With this novel approach in hand, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the resulting discrete sequential GAN on multimodal activity anticipation. We evaluate the approach on three standard datasets and show that it outperforms previous approaches in terms of both accuracy and diversity, thereby yielding a new state-of-the-art in activity anticipation. |
| [pdf][code:TBA] |
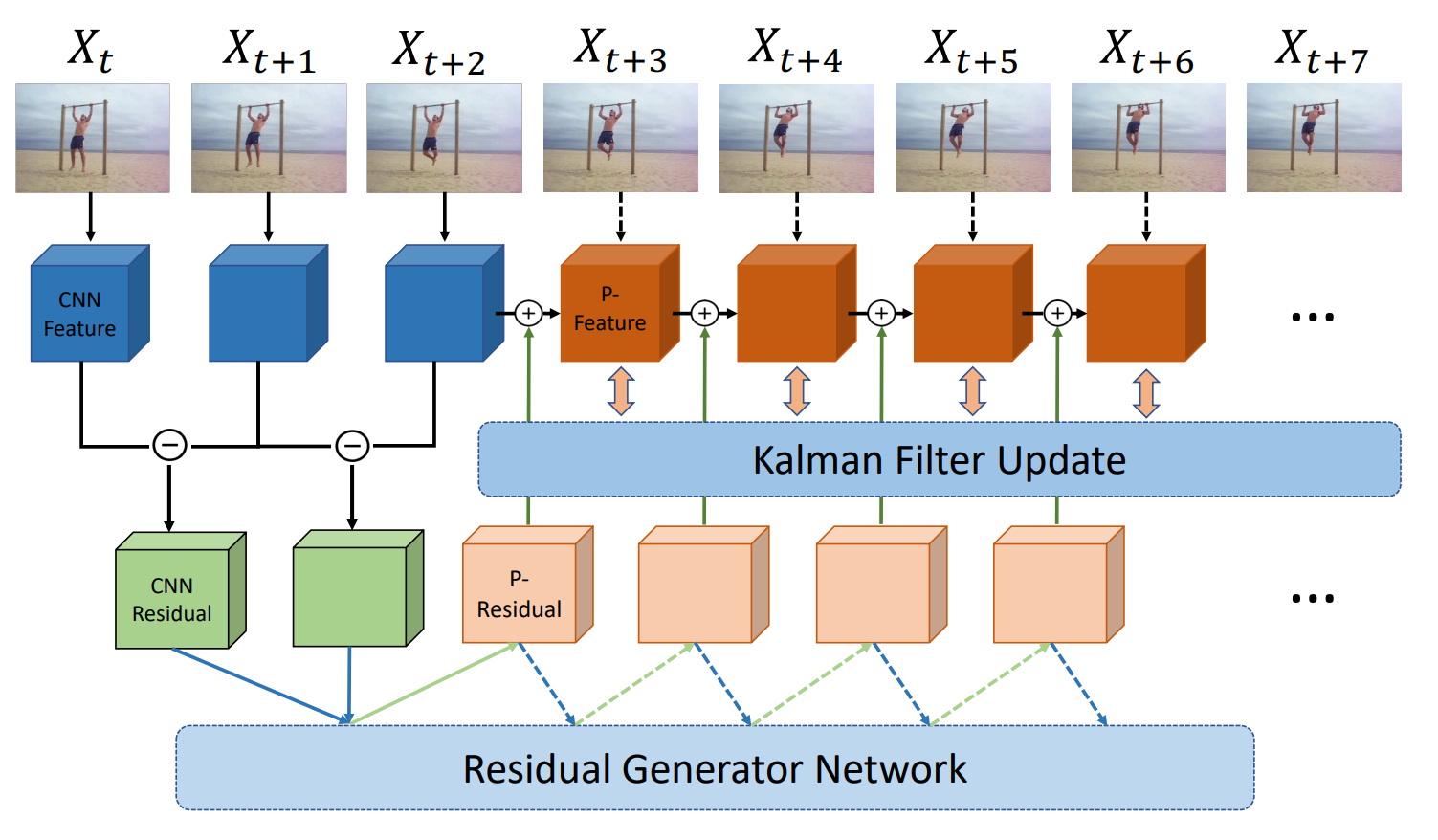
Spatiotemporal Feature Residual Propagation for Action Prediction
He Zhao, Richard P. Wildes
International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2019)
 | Recognizing actions from limited preliminary video observations has seen considerable recent progress. Typically, however, such progress has been had without explicitly modeling fine-grained motion evolution as a potentially valuable information source. We address this task by investigating how action patterns evolve over time in a spatial feature space. There are three key components to our system. First, we work with intermediate-layer ConvNet features, which allow for abstraction from raw data, while retaining spatial layout, which is sacrificed in approaches that rely on vectorized global representations. Second, instead of propagating features per se, we propagate their residuals across time, which allows for a compact representation that reduces redundancy while retaining essential information about evolution over time. Third, we employ a Kalman filter to combat error build-up and unify across prediction start times. |
| [pdf][code] |
Construction Scene DPM Object Tracking via Detection
He Zhao, Pingjun Chen, Lin Yang
  | Built a Local Binary Patterns based software for face recogition, together with Deformable Part Model for object tracking. Implementation these two effective algorithms for contruction site videos with the aim to prevent from stranger invading and fire-fighting equipments stealing. Now we are heading towards implementing MOT on large-scale construction site video to monitor multiple objects. |
Deep Convolution Neural Network for Muscle Cell Segmentation
He Zhao, Shaoju Wu, Lin Yang
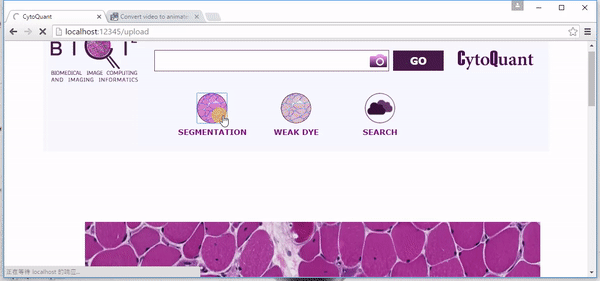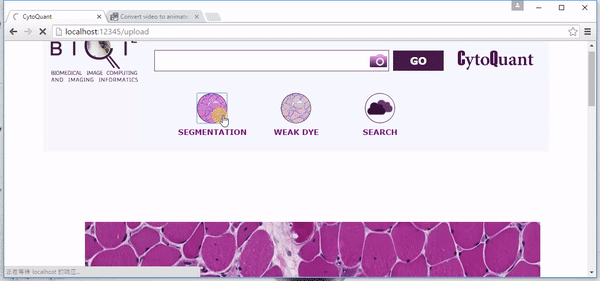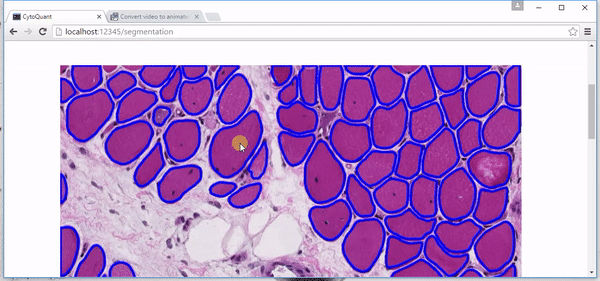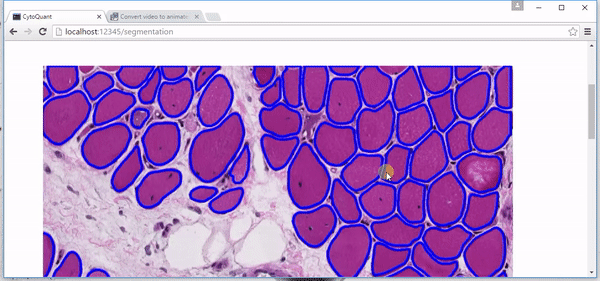 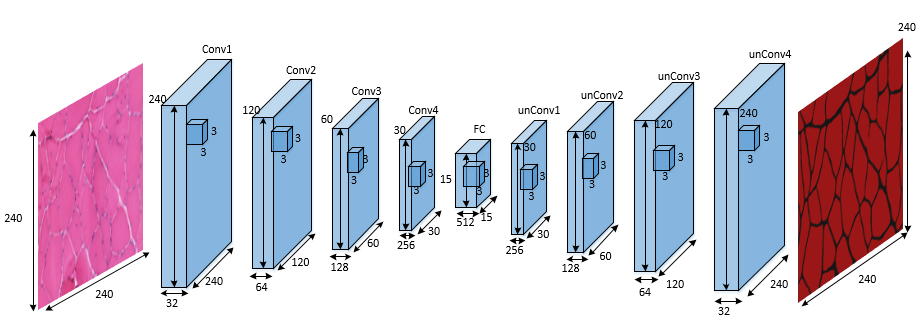 | Based on medical image data provided by BICI2 lab, implemented fully connected network edge detection methods with watershad as post-proecess and got a better detection and segmentation effect compared with random forest method. Now working on residual neural network to achieve better result and keep digging on deep learning. |
Random Forest Muscle Cell Segmentation
He Zhao, Shaoju Wu, Pingjun Chen, Mason, Lin Yang
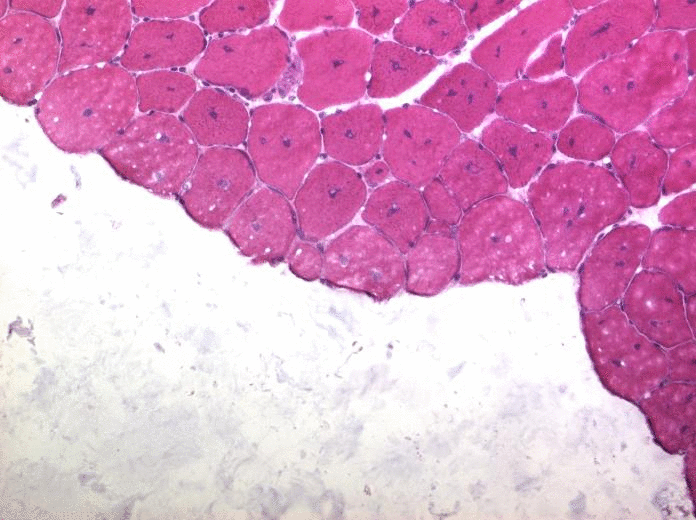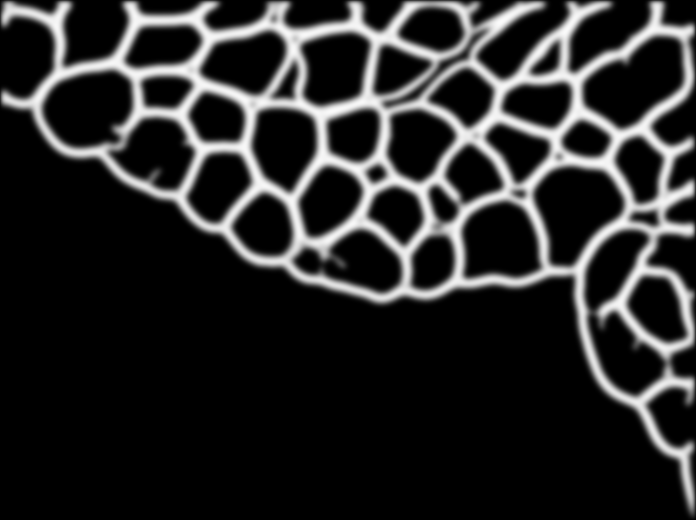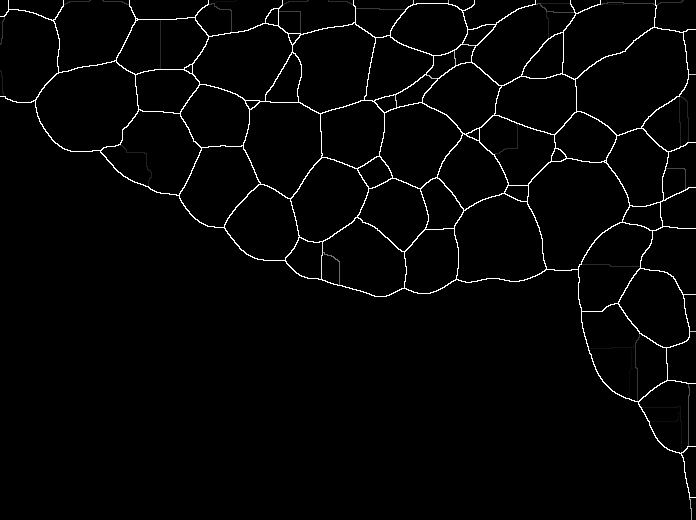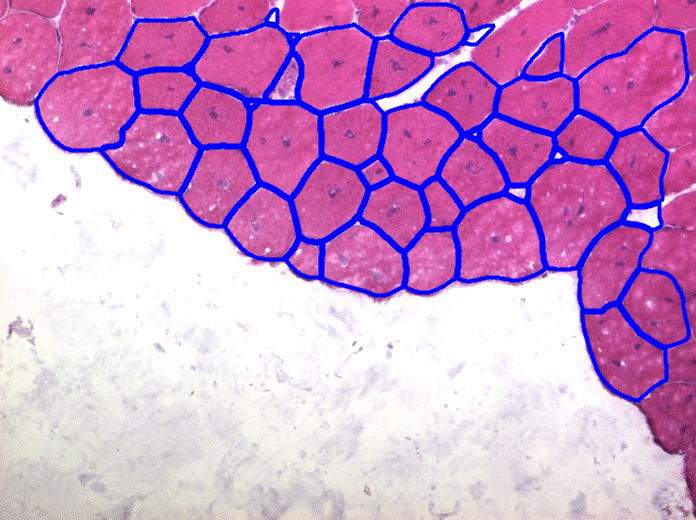 | Developed a cpp software implementation of an image segmentation algorithm based on paper 'Fast Edge Detection Using Structured Forests'(Piotr Dollár), for Muscle Cell Image gathered from University of Florida Shands Hospital. Combined with HOG(Histogram of oriented gradients) for feature extraction, UCM Segmentation algorithm, Watershed and self-defined Hierarchical segmentation framework for segmentation, this cpp dll-call software works quite well for our muscle cell data and totally get rid of matlab dependency. |
Online Muscle Cell Annotation Tool
Pingjun Chen, He Zhao, Manish, Lin Yang
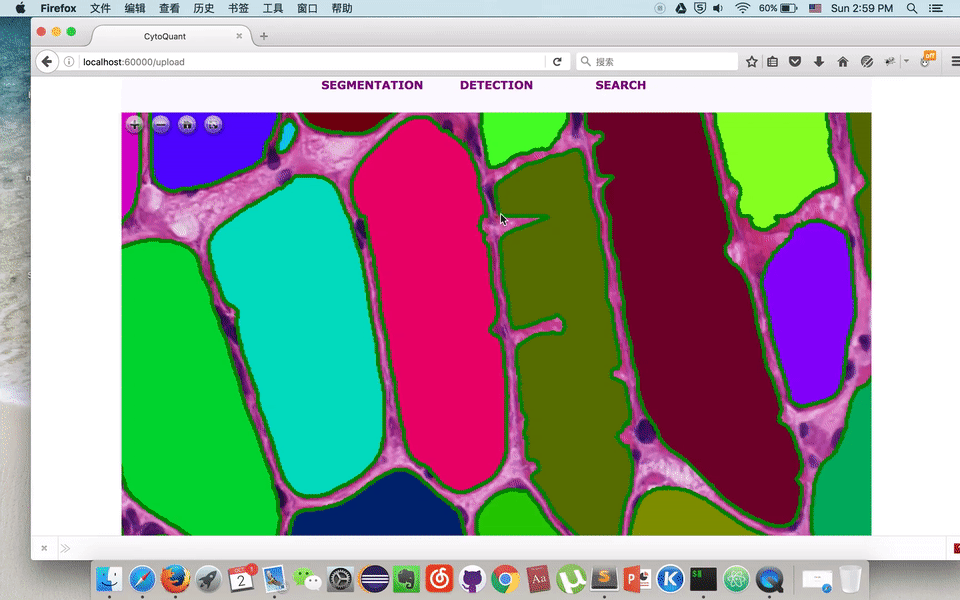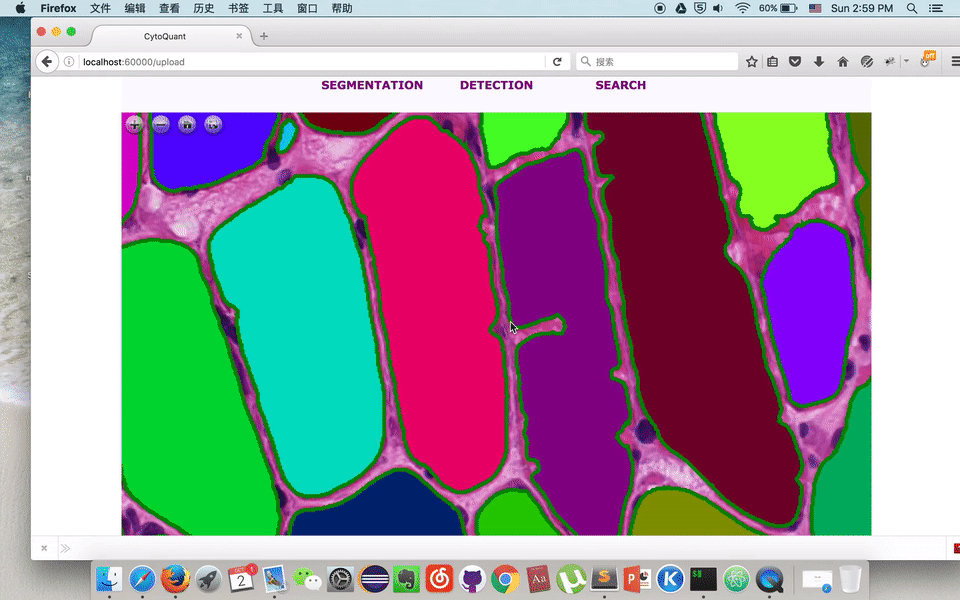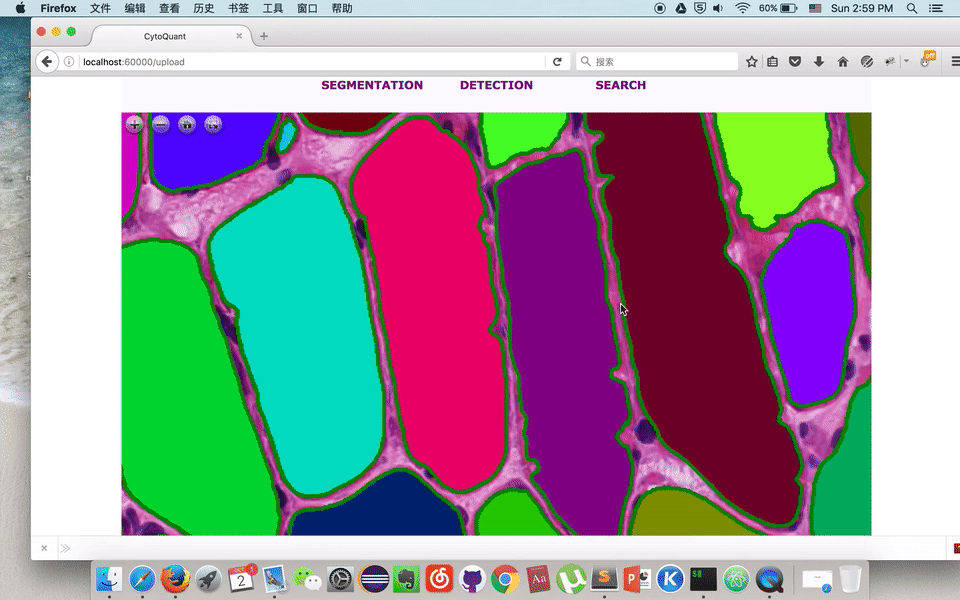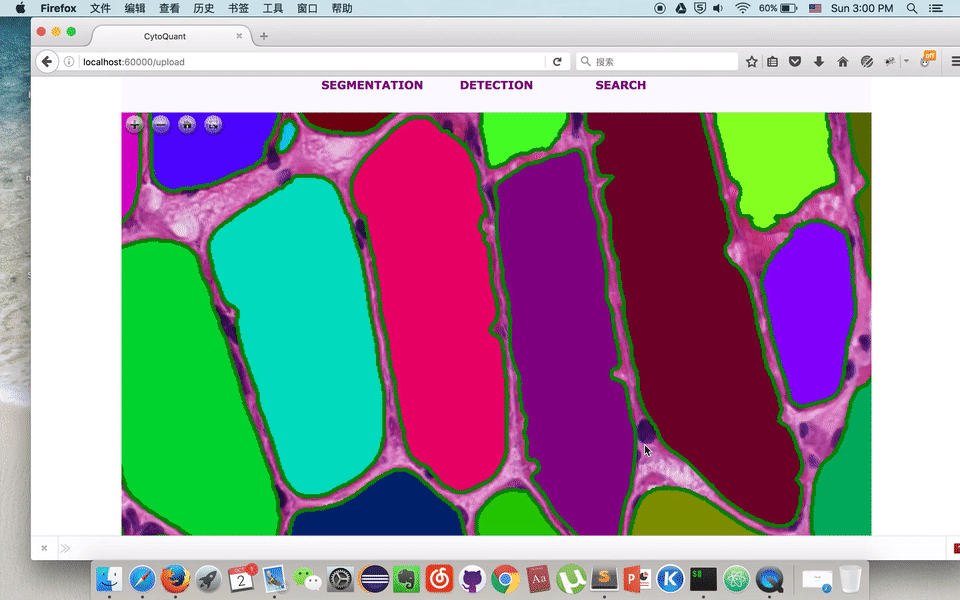 | Using python FLASK framework to build up an online platform, which utilizes our recent accomplishments on Cell-Image Segmentation Research. And allows everyone to modify the contour as groundtruth for further training in deep learning. With Flask's strong server-client interaction functionality, visitors would be able to modify the contour of cell online and re-submit it back to server. To make it more interactive, we use deep zoom package, paper.js and openseadragon as well. |







